针对广域网流量和数据中心流量在数据中心内部共享bottleneck带来的性能问题
Core idea
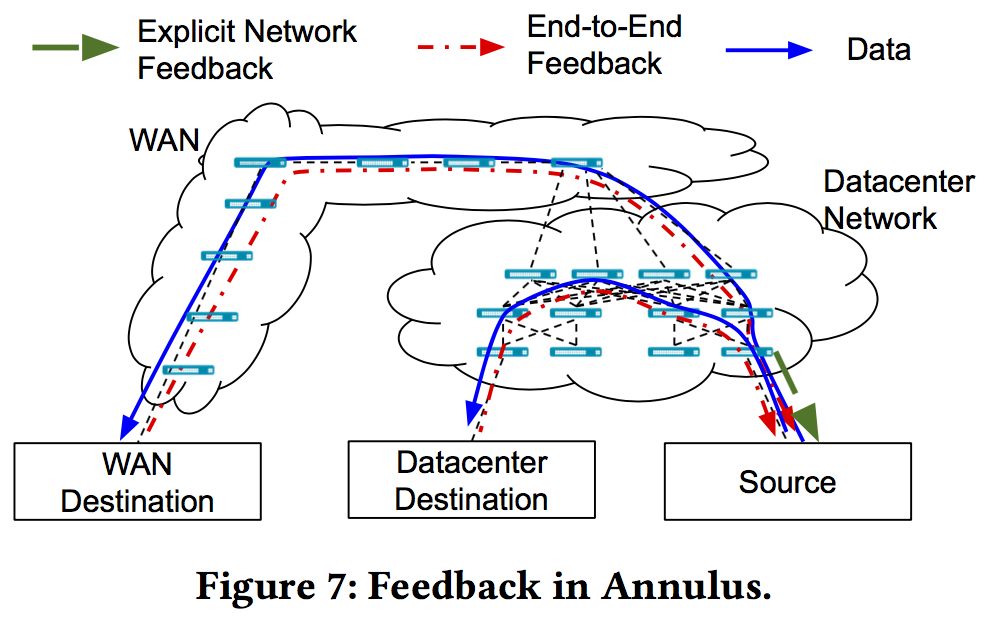
两个control loop,主要目的是让广域网的流量能够及时获知带宽变化,进行速率调节:
- congestion at nearby datacenter switches (e.g. ToRs) configured to send direct feedback; 借助于QCN 让交换机直接发送反馈
- congestion at other WAN or datacenter switches that do not send direct feedback; 使用已有拥塞控制协议
Motivation
作者采用实际流量观察 + 仿真验证的方式说明问题。
WAN的RTT长(ms)DC的RTT短 (us)二者不同control loop交互带来性能问题:
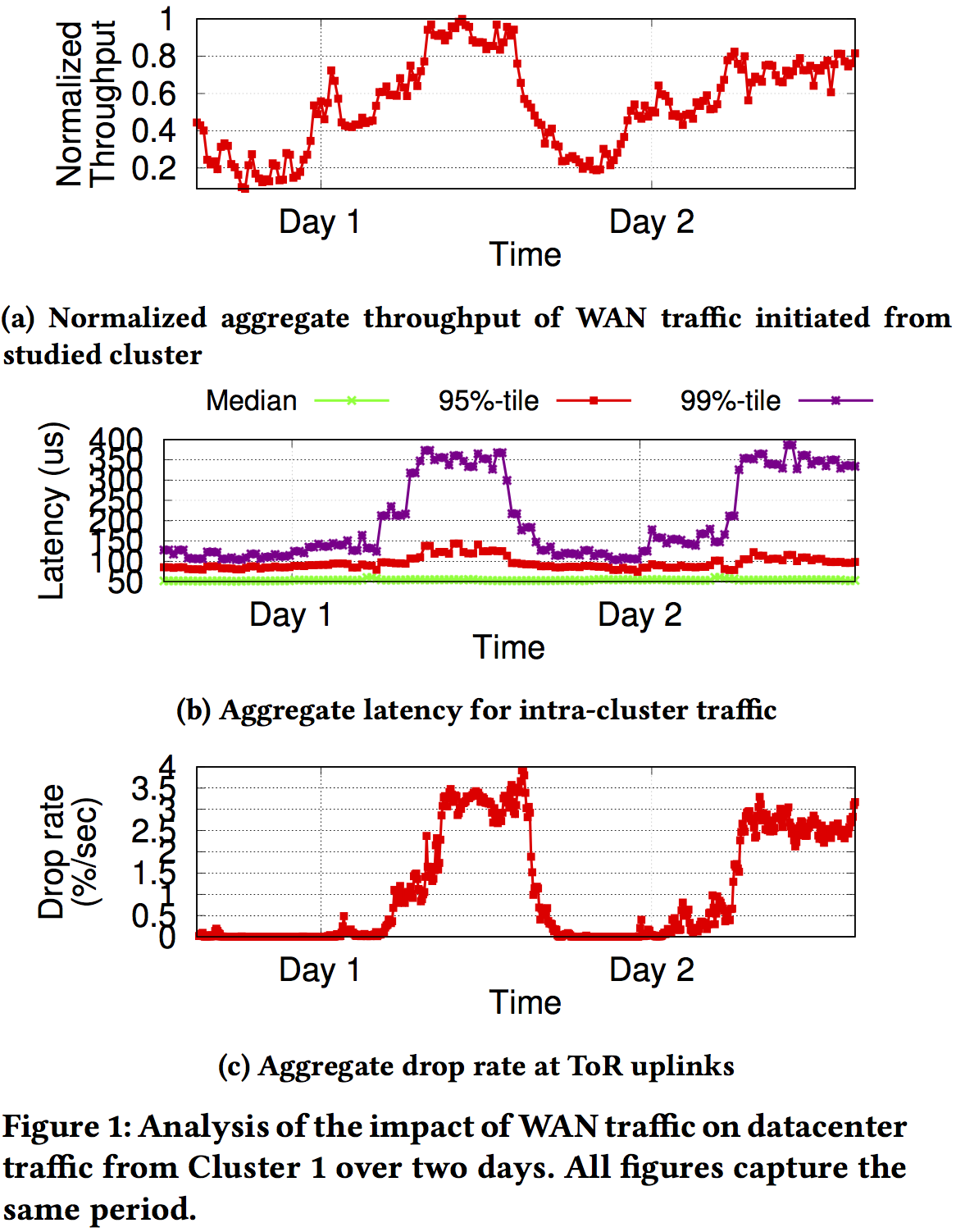
根本原因:long feedback delay of WAN congestion control and the small buffer space in datacenter switches
导致后果: 1) datacenter traffic reacts much faster, taking the full burden of slowing down to drain the queues while facing long queues caused by the slow reacting WAN traffic.
2) feedback for the WAN traffic lags behind changes in capacity, making it difficult for the WAN congestion control to track available bandwidth accurately
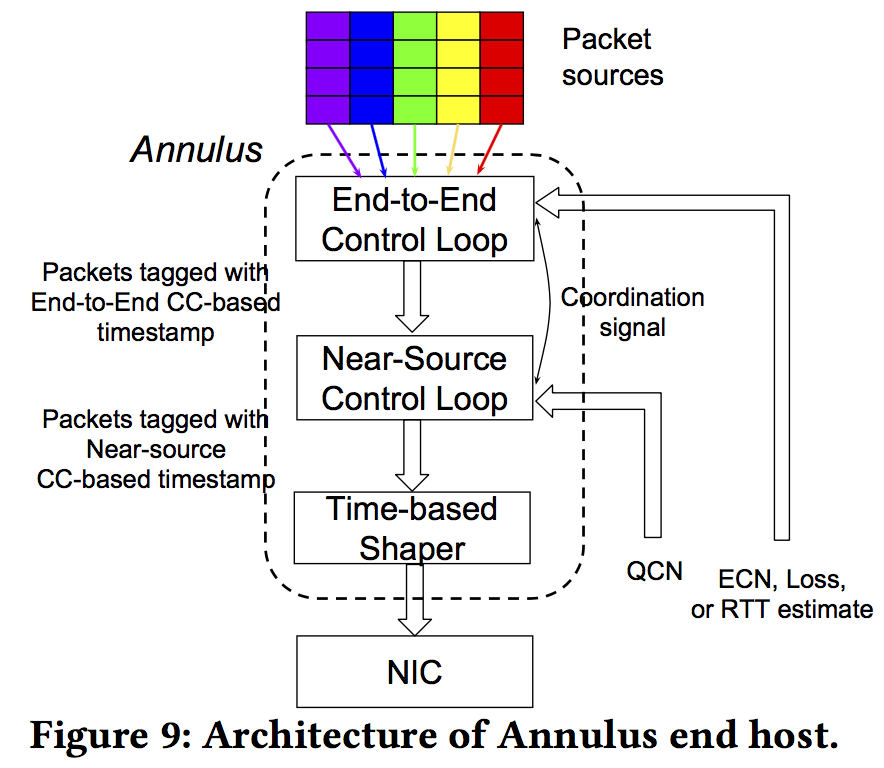
Design
速率取两个control loop算出的最小速率
Implementation and Evaluation
Thoughts
-
个人觉得这篇文章的idea其实不是很novel (有一种自己做的话其实也这么做的感觉), 解决的这个问题也不是一个别人想不到的问题。但是工作做的比较扎实, 论述有理有据, 这其实也不是有了想法每个人都能做到的。 还是要好好向 Mohammad Alizadeh 组的文章学习写作~
-
“near source control”
参考文献
Annulus: A Dual Congestion Control Loop for Datacenter and WAN Traffic Aggregates