核心思想
专门用于快速检测丢包以及获取丢包详细信息的monitor system. 可以说是第一篇专门做数据中心丢包troubleshooting的文章,007在此文章之后.
Packet Loss Background
-
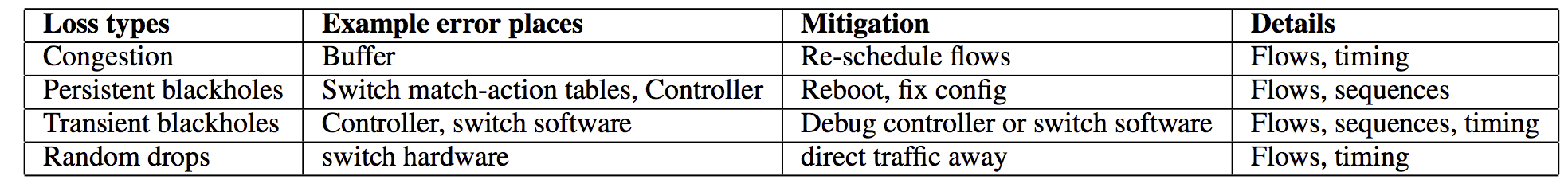
丢包很常见并且对数据中心应用影响大:on average in a production data center for one year, up to 40-80 machines can experience packet losses, 4 network maintenance jobs can cause 30-minute random connectivity losses, and 3 router failures can cause immediate traffic blackholing for an hour. 数据中心常见丢包分类:
- 拥塞丢包
- 黑洞(持续性、暂态):匹配到某个特定’pattern’的数据包被丢弃. 持续性黑洞一般是由于match-action table corruption或控制器规则配置错误引起, 暂态黑洞一般是由于非原子的规则更新或者网络范围内更新不一致引起.
- 随机丢包:交换机随机丢弃数据包without report. 可能是由于有故障的linecard或者link.
-
丢包检测的需求:
- Fast detection: 只有快速检测才能更快narrow down root cause 和诊断. 减少丢包影响.
- Generic detection of all loss types: 丢包原因很多
- Capturing location information: 知道具体位置才能快速采取action, 交换机 link 还是 host NIC
- Capturing packet header information: 需要区分丢包原因采取针对性措施,因此很多详细信息必不可少:五元组,timing,loss pattern等.
-
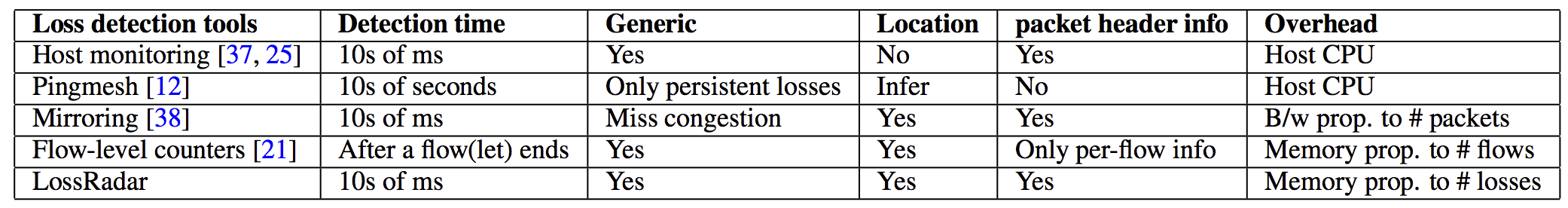
已有方案的不足:
- End host based solutions: 准确定位丢包位置困难. Pingmesh可以推断丢包位置,但是不能与应用关联,不能区分丢包原因,并且probe的频率太低. (007发表于这片文章之后,已经能够定位link,与应用关联,但是不能区分丢包原因)
- Packet mirroring at switches: 漏掉丢包类型和数量
- Counters at switches: 因为丢包原因多种并且不确定,很难提前配置好对应的counter. FlowRadar(NSDI 2016)使用per-flow的counter,但是需要多交换机的counter对比同步才能知道丢包,并且存储消耗与monitor的流数目成正比.
Design Overview
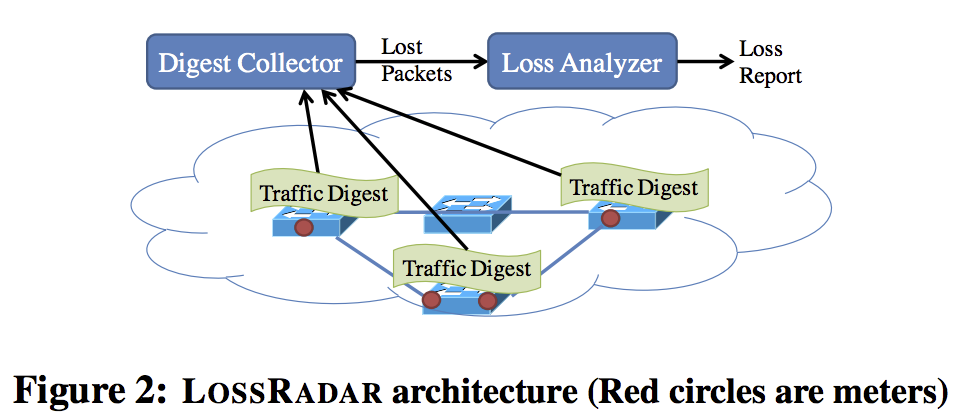
设计分别针对丢包检测的需求.
-
Generic to all types of losses:利用
Flow Conservation Rule: The set of packets that comes into any network domain (a link, a switch module, a switch, or an area of network devices) should be equal to the set of packets that leaves the domain, as long as the domain does not include any packet sources and sinks. -
Fast detection of losses and their locations:利用
meters(upstream and downstream meters). Each meter encodes the unique identifiers for individual packets into a traffic digest, and periodically reports traffic digests to a central LOSSRADAR collector. -
Capture packet header information with low overhead:利用 a
traffic digestwhose size is proportional to the number of packet losses independent of the total traffic or flows in the system.
Challenges
- Small size digests: digest需要记录足够多信息并且overhead尽量小
- Meter placement: 解决meter的placement问题,部分部署
- Loss analyzer: 诊断root cause
Traffic digest
通过upstream and downstream meters记录的信息对比,就能够筛选出lost packets,只需要存储lost packets的信息. 实现方法:Invertible Bloom Filter.
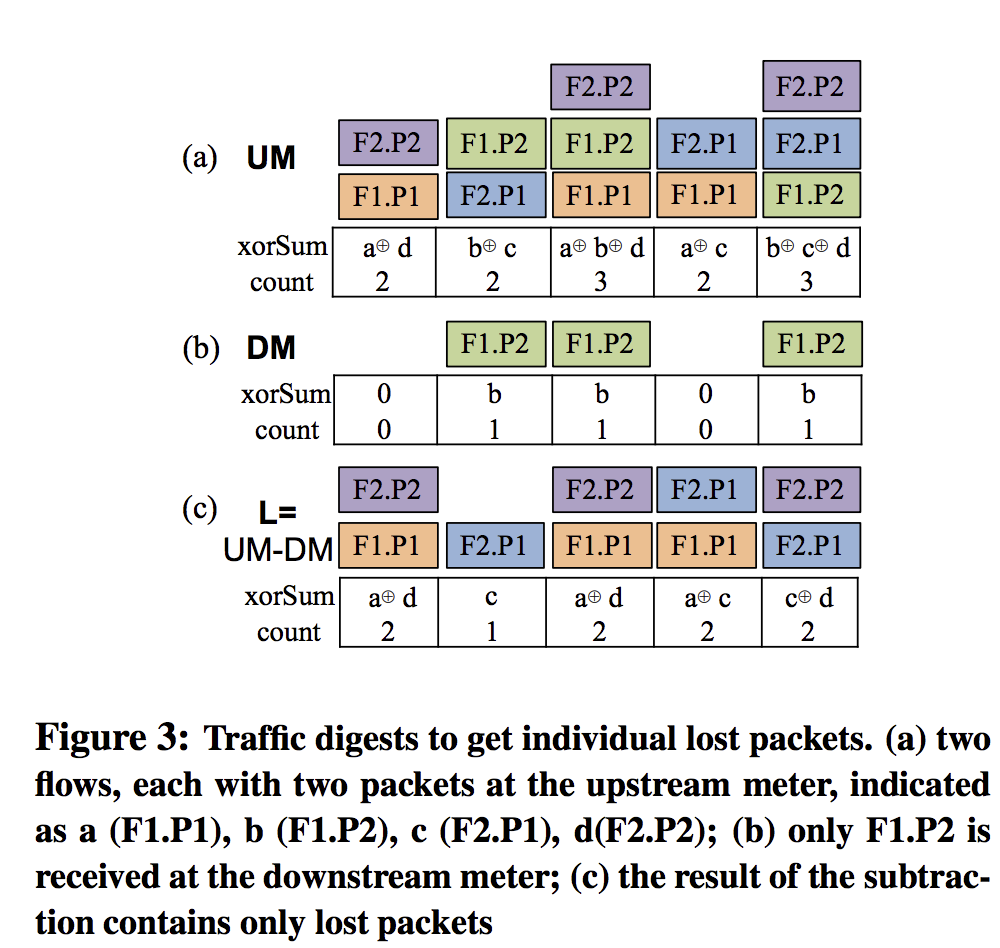
digest里还可以包含其他信息:默认包括五元组,IP_ID(用于标识数据包). 其他flag信息等也可以
measurement batch:每隔$T$时间将digest信息上传. 每个数据包携带一个batch_ID区分batch. 为了应对数据包存在乱序,下游的meter $T + timeout$
Network Wide Deployment
- 全网部署:
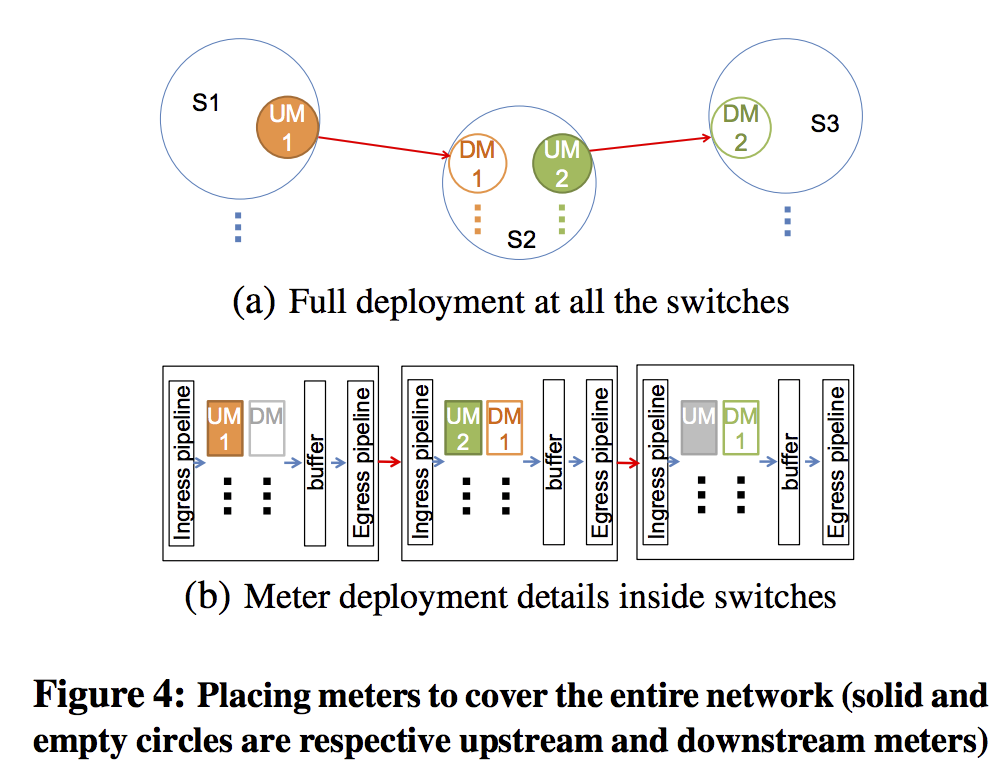
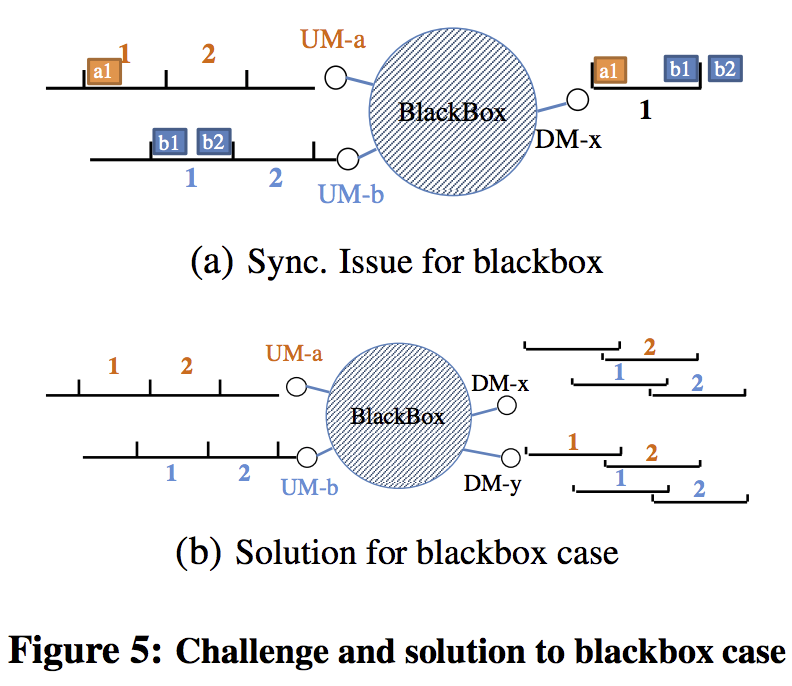
- 增量部署:把未部署的部分看做一个Blackbox. unsynchronized clock问题. Each downstream meter maintains separate digests for each upstream meter. To detect the packet losses, we can add up all the digests for the same upstream meter across all the downstream meters (e.g., the digests for UM-a’s batch 1 at DM-x and DM-y respectively), and compare the sum with the digest at the upstream meter (e.g., UM-a’s batch 1).
Loss Analyzer
假设: In a short time (e.g. 10 ms) at one switch, we assume losses are dominated by one reason.
-
Root cause analyzer
根据loss pattern区分丢包类型:
- Congestion: bursty, and the gap between back-to-back losses is only a few microseconds.
- Blackholes: 三种情况: Bursty and consecutive losses within a flow; Non-bursty and consecutive losses within a flow; Only a SYN packet loss from each flow.
- Random drops: evenly distributed over time.
- Loop: TTL = 0.


-
ACL rule corruption analyzer
只考虑one-bit flip的情况. 三种情况:
- a deny rule’s match field corrupted, so it denies flows originally not covered by it;
- an accept rule’s match field corrupted, and the flows originally covered by it now match other deny rules;
- an accept rule’s action changes to deny.
Implementation and evaluation
Open vSwitch 和 P4 behavioral model 实现. Each meter reports the digests every 10ms.
实验充分
-
Bandwidth and memory overhead
(1)Bandwidth usage of LOSSRADAR is much less than full packet mirroring.节省99.5%带宽(loss rate 0.1%).
(2)LOSSRADAR saves memory when the number of concurrent flow is large or loss rate is low, compared with FlowRadar.
-
Detection and inference effectiveness
The precision is close to 100%
- Memory usage in partial deployments
- Detection latency: testbed. 12ms之内
-
LOSSRADAR applications
(1)引入black hole和random packet drop,loss radar检测到后快速进行重路由,提升流吞吐;
(2)Correlating lost packets with ACLs;
参考文献
LossRadar: Fast Detection of Lost Packets in Data Center Networks