核心思想
设计了一种新的分布式机器学习(DML)参数同步算法。最大意义在于说明了拓扑对参数同步算法提供了优化空间。
Background and Motivation
已有的参数同步算法:
- PS-based synchronization (PS). 集中式, 较为常用(Tensorflow, Caffe, MXNet等). 两种角色: 参数服务器(Paremeter server)和 worker. Worker: push and pull模式. Worker生成参数的gradients, push给参数服务器, 参数服务器aggregate the gradients等待workers to pull them back.
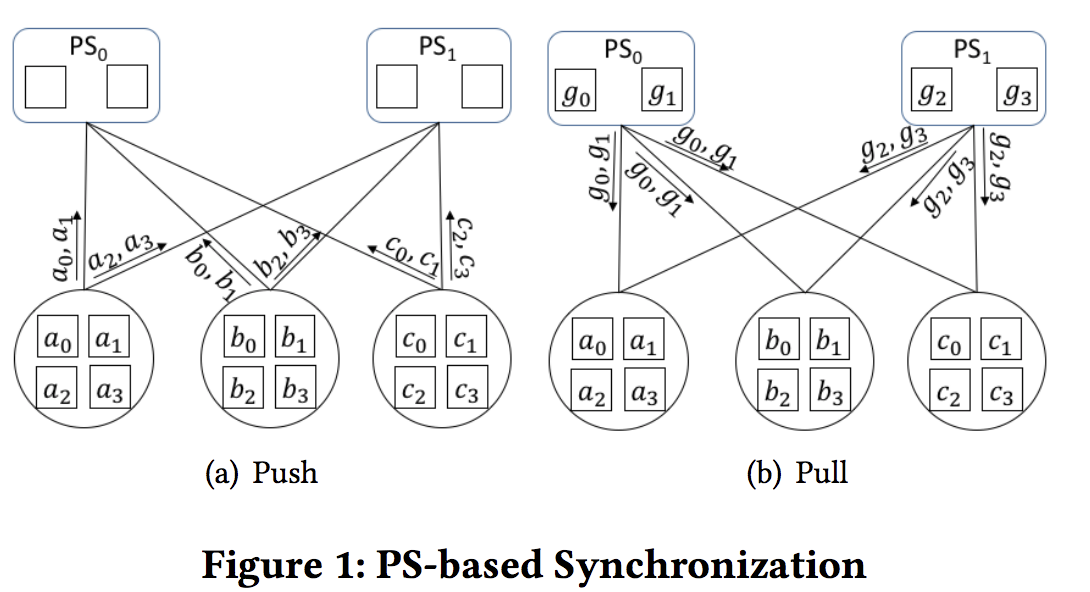
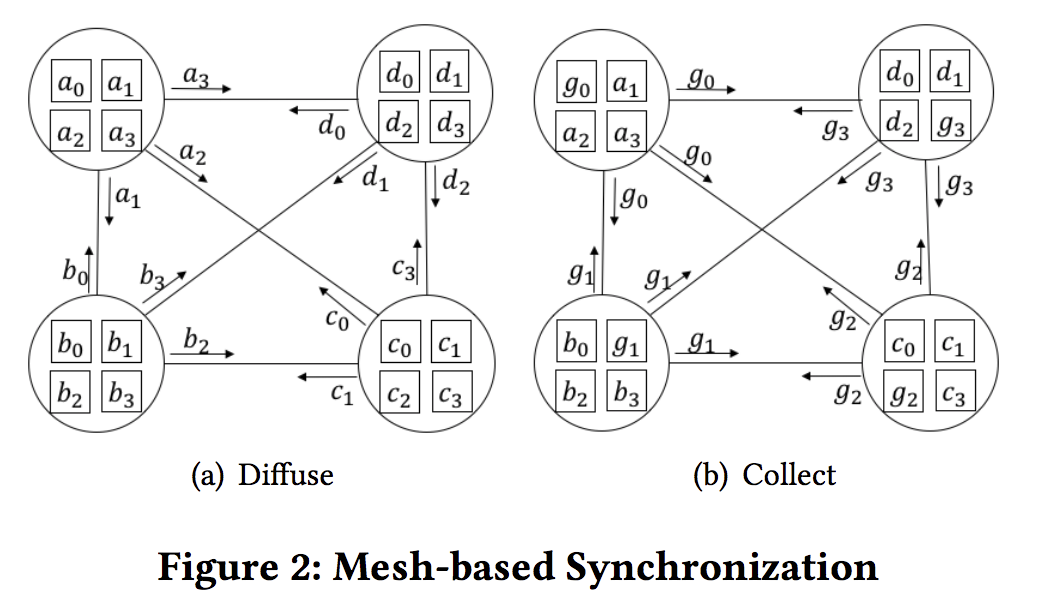
- Mesh-based synchronization (MS). 分布式. 服务器没有功能性区分. 工作模式: diffuse + collect.
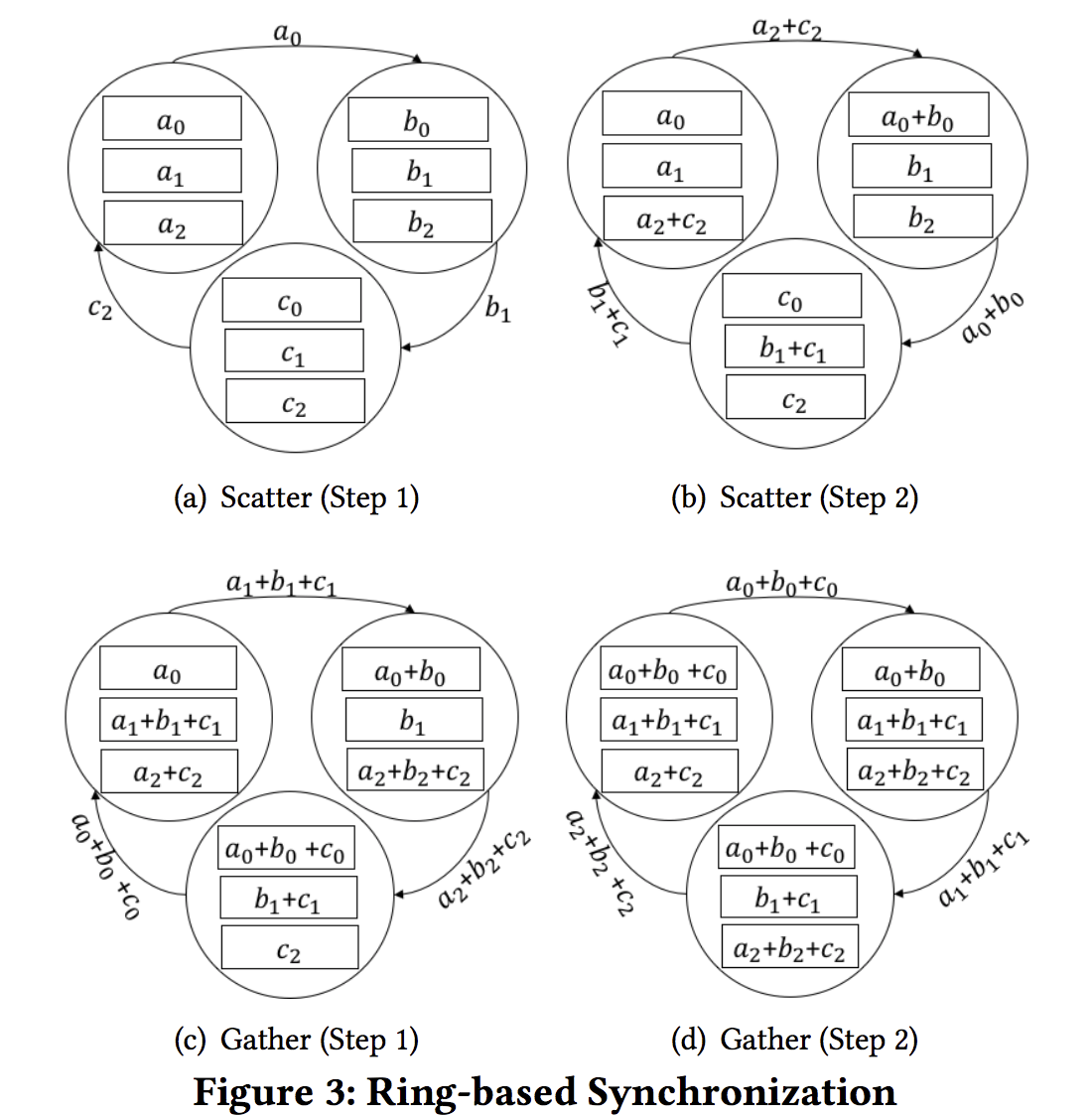
- Ring-based synchronization (RS).分布式. 工作模式: scatter + gather. 每个server只与一个server和receiver通信.
已有的这些Flat的参数同步算法在大规模网络的问题:
-
PS: 由于通常由CLOS网络构建, 不可能所有server与参数服务器都在一个rack下, 必然存在跨Rack通信, 会有RDMA的一些问题: PFC deadlock, congestion spreading.
本质上是RDMA的拥塞控制在大规模网络的问题 -
MS 和 RS: 如果用Fat-tree这类CLOS网络构建, 问题与PS的相同。如果构建相应的物理拓扑网络, 不实际: MS需要N个服务器每个有N-1块网卡. RS ring的大规模网络鲁棒性差。
Design
-
采用 server-centric (Bcube、DCell、Torus等)而不是 Fat-tree 这类 switch-centric的物理拓扑: server-centric最重要的优势是交换机不是直连的, RDMA的PFC最多只会传递一跳, 而server有足够大的buffer去吸收, 因此不会出现CLOS网络下PFC的死锁问题.
server-centic:服务器和交换价都具有转发功能; switch-centric:只有交换机具有转发功能
-
Synchronization is divided into multiple stages. Each stage possesses two parts (i.e. push+pull or diffuse+collect or scatter+gather) to complete a specific synchronization algorithm, and servers aggregates the partial results before entering the higher-stage synchronization.

Implementation and evaluation
理论计算global synchronization time (GST). 在Bcube、Torus拓扑下比较HiPS PS MS RS.
参考文献
HiPS: Hierarchical Parameter Synchronization in Large-Scale Distributed Machine Learning