核心思想
设计一个能够基于任何支持优先级调度的传输协议的coflow调度机制。最大的贡献是理论证明了:只要给定一个合适的coflow的ordering, 任何per-flow的rate allocation按照这个ordering优先级调度, 都能够达到平均coflow完成时间是最优调度的4$\times$以内。
Motivation: 以前的coflow调度机制(Varys, Aalo等), 其核心思想都是控制器知道每个coflow的相关信息(source port,destination port,size等), 然后根据可用带宽给每个coflow分配速率(包括coflow内每条流的速率分配), 然后enforce到端, 当新的coflow到达或结束时重新计算。这种方式很大的一个问题是实际中需要对每条流进行速率分配, 开销大. 因此Sincronia的思想就是解除per-flow rate allocation这个限制, 将rate allocation和具体的优先级调度下放到底层传输协议完成。
Design
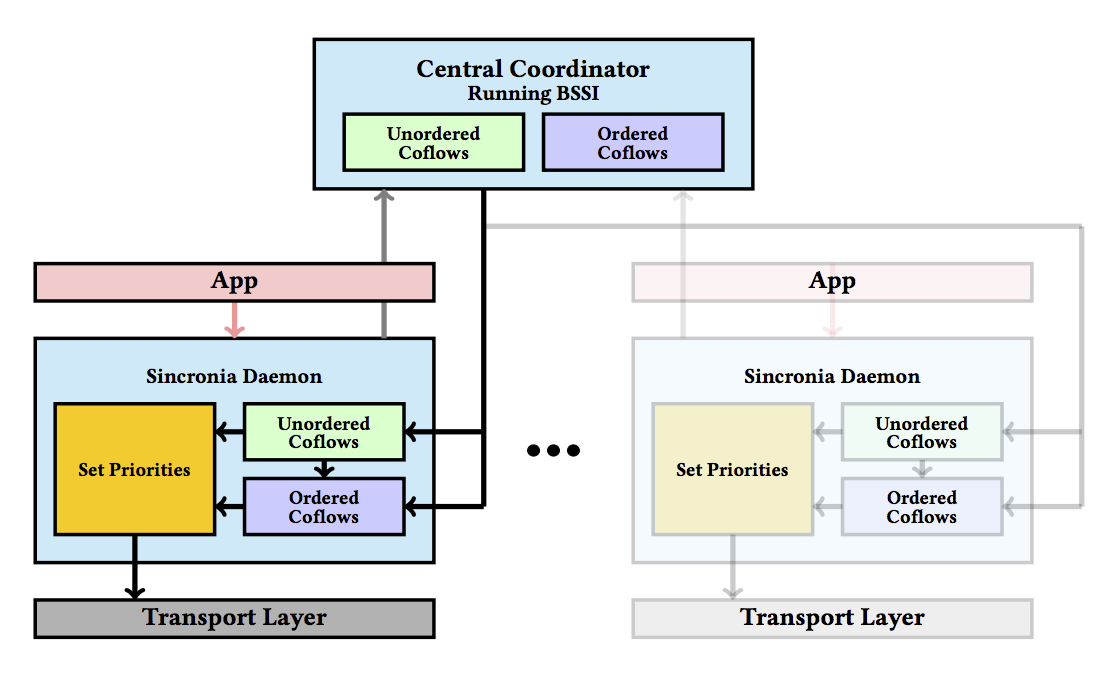
核心算法有两个, 一个是确定coflow的ordering, 一个是如何从offline算法转化为online算法
-
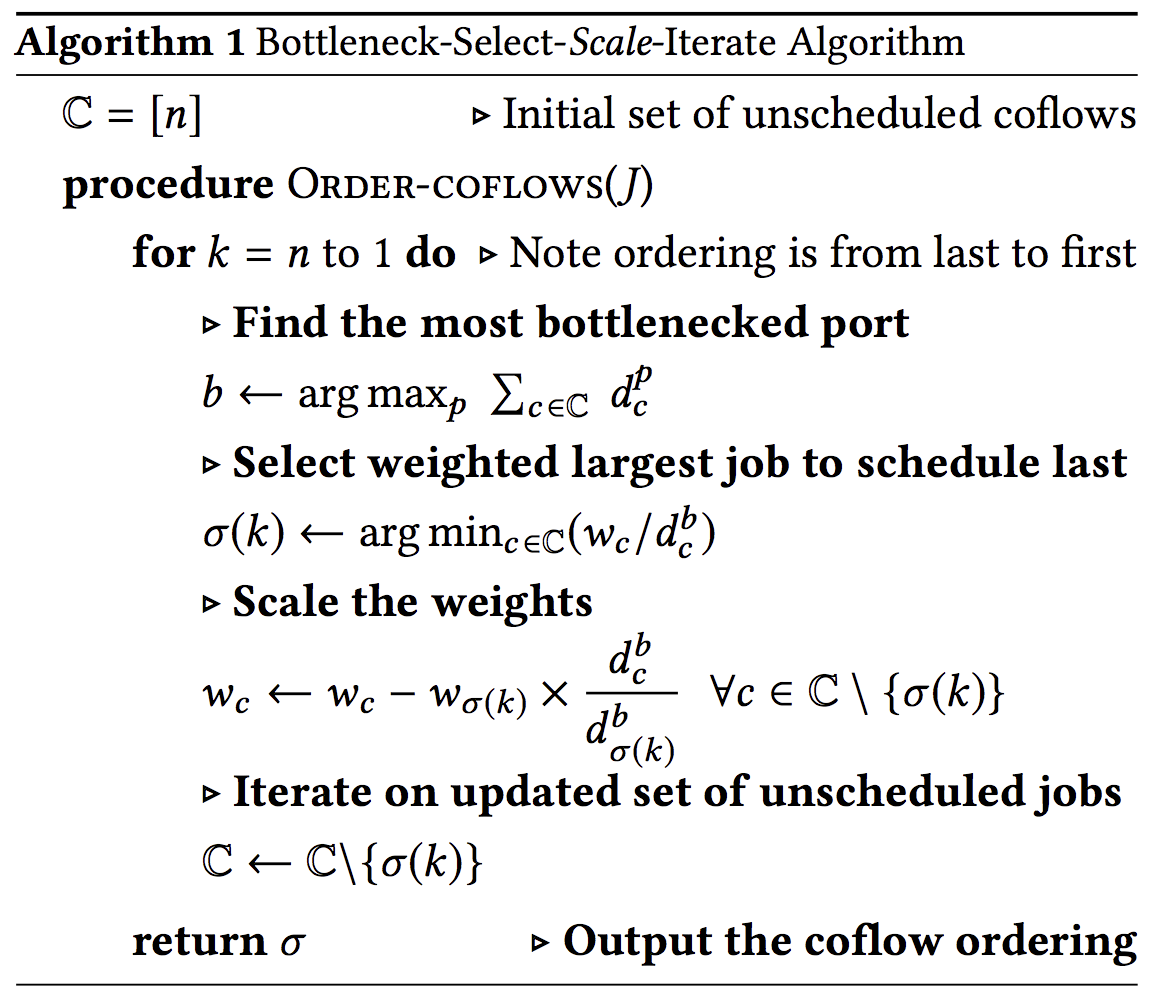
Coflow ordering: primal-dual based greedy algorithm. Bottleneck-Select-Scale-Iterate (BSSI)
本质上还是逼近shortest remaining time first原则。 四步:
bottleneck: finds the most bottlenecked ingress or egress port;select: it chooses the coflow with largest remaining weighted processing time at port b and places this coflow the last among all unordered coflows;scale: scales the weights of all unordered coflows to capture how ordering the coflow chosen in the second step impacts the completion time of all remaining coflows;iterate: simply iterate on the set of unordered flows until all coflows are ordered.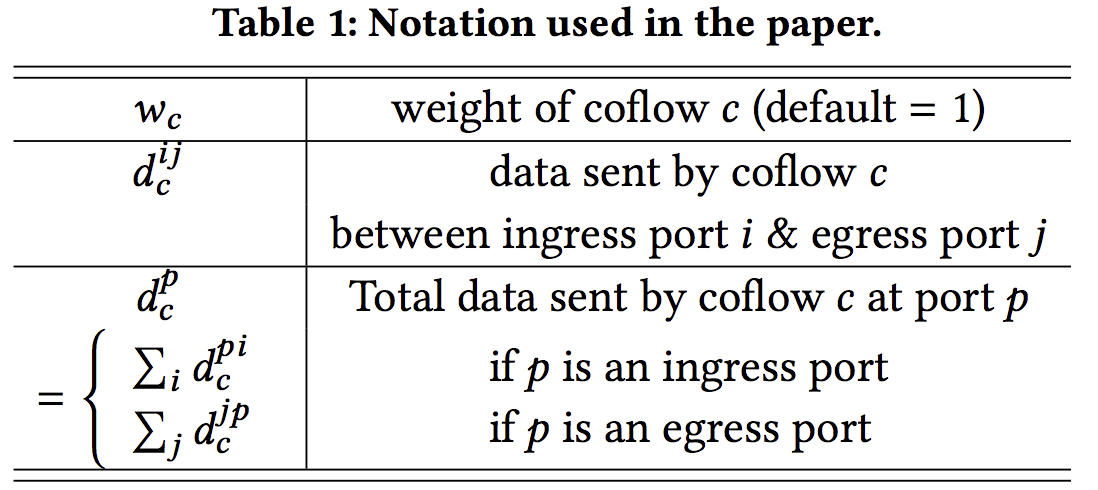
-
From offline to online
(1) Time is divided into exponentially increasing sized epochs;
(2) In each epoch, a subset of unfinished coflows are selected and “ordered” using a simple greedy algorithm;
(3) Each host independently sets a priority for its flows (based on the corresponding coflow’s ordering), and offloads the flow to underlying priority-enabled transport mechanism;
(4) Coflows that arrive between epoch boundaries are greedily scheduled for work conservation.
Proof
Implementation and evaluation
-
Testbed.
-
Simulations.
My thinking
仍然需要知道size等先验信息